Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
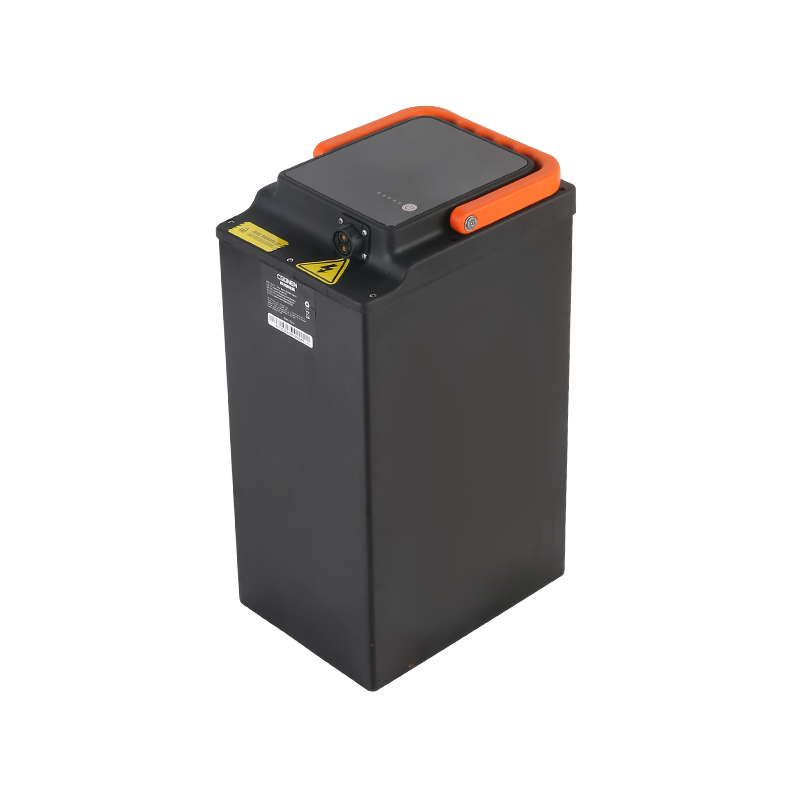
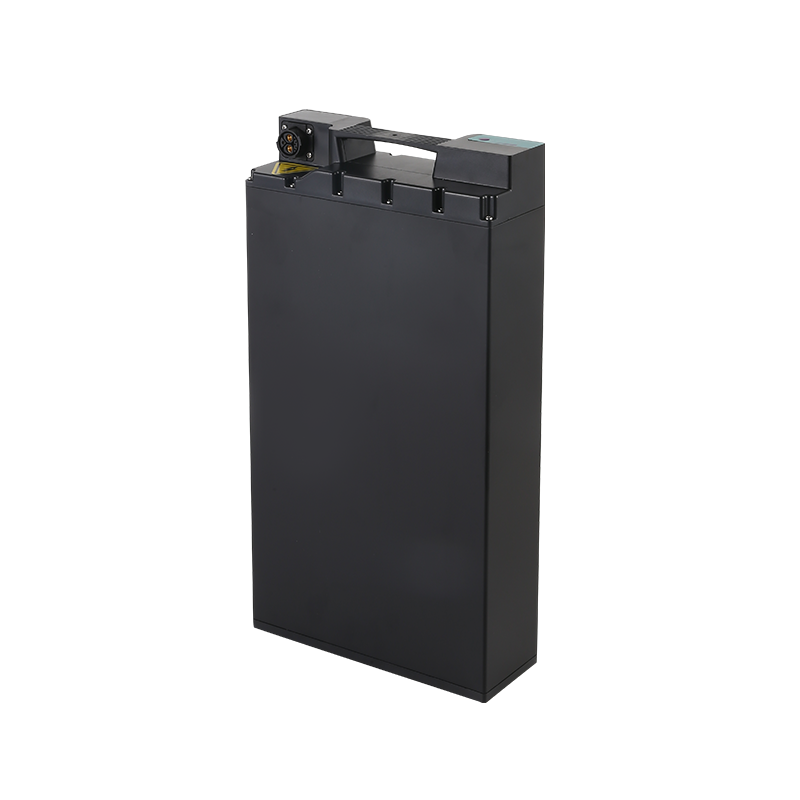
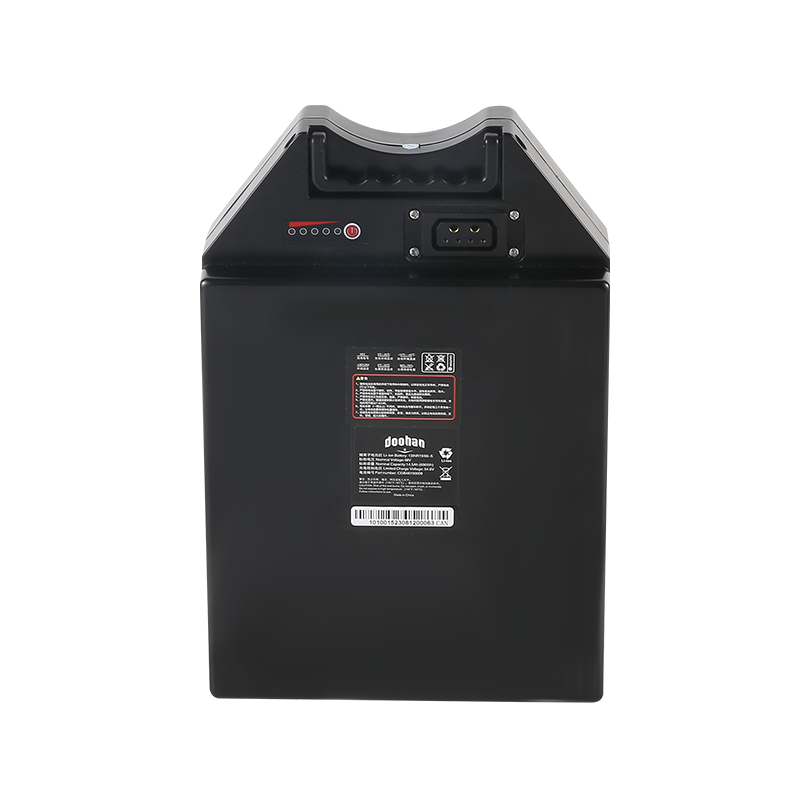
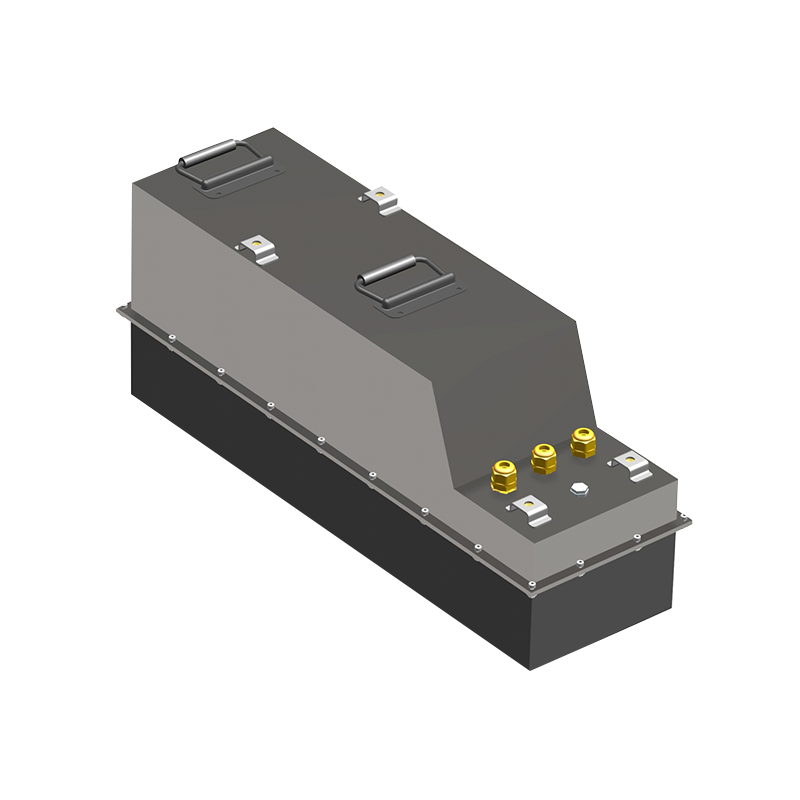
Key Characteristics of Light Electric Vehicle Batteries
The growing popularity of light electric vehicles (LEVs), such as electric bicycles, scooters, and small cars, has shifted the focus toward efficient, lightweight, and reliable battery technology.
Batteries serve as the heart of any electric vehicle, providing the energy needed to power the motor and keep the vehicle running. In light electric vehicles, battery size, weight, and energy capacity are crucial factors in determining their overall performance, range, and usability. Since LEVs are typically designed for short trips, urban commuting, or recreational purposes, their batteries need to balance lightweight construction with sufficient energy storage to ensure they are practical and efficient.
In addition to powering the vehicle, batteries in LEVs also influence key features such as charging time, cost, and the environmental impact of the vehicle. As a result, choosing the right battery is essential to ensuring the vehicle’s reliability and efficiency.
Characteristics of LEV Batteries:
Energy Density: Energy density refers to the amount of energy stored per unit weight or volume of the battery. For light electric vehicles, high energy density is important to provide longer ranges without increasing the vehicle's weight significantly. Higher energy density allows for better performance while keeping the vehicle light and agile.
Cycle Life: The cycle life of a battery is the number of charge and discharge cycles it can undergo before its capacity starts to degrade. For LEVs, batteries with a long cycle life are preferred, as they can last longer and require fewer replacements, ultimately making the vehicle more economical and sustainable.
Charging Speed: The time it takes to fully charge the battery is another important factor. Quick charging batteries are ideal for urban commuting, where short charging breaks are needed between trips. Faster charging times improve the convenience of using LEVs for daily transportation.
Safety: Safety is paramount when selecting batteries for electric vehicles. Overcharging, overheating, or physical damage to batteries candangerous situations. Batteries with built-in safety mechanisms, such as temperature control and protection against overcharging, are essential for ensuring safe operation in LEVs.
Types of Batteries Used in LEVs:
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the more common type used in light electric vehicles due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively lightweight design. Li-ion batteries provide efficient power output and are widely used in electric bicycles, scooters, and compact electric cars. They are more expensive than other types of batteries, but their performance justifies the cost for many LEV users.
Lead-Acid Batteries: While less commonly used in modern LEVs due to their heavier weight and shorter lifespan, lead-acid batteries are still found in some budget-friendly electric vehicles. These batteries are more affordable, but they generally have lower energy density and a shorter cycle life compared to lithium-ion options. They are more suitable for short-range, low-speed vehicles or those used for recreational purposes.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: NiMH batteries are another alternative to lithium-ion, offering a balance between energy density and affordability. They are generally heavier than lithium-ion batteries but are less expensive, making them a choice for certain LEVs. They also have a relatively longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries, though they are still less efficient than Li-ion options.
The battery is a critical component in the performance and efficiency of light electric vehicles. With a wide range of battery types and considerations, including energy density, cycle life, and cost, it is essential to choose a battery that fits the specific needs of the vehicle and the user.
-

+86-13049701086
-

Stonehuang@CGONEN.com
-

No.88, Huji Road, Taizhou Bay Binhai New Area, Jiaojiang District, Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China